Hey Travel From the Heart to a Capillary Bed and Back to the Heart Again
Circulation Worksheet Answers
From WikiEducator
Jump to: navigation, search
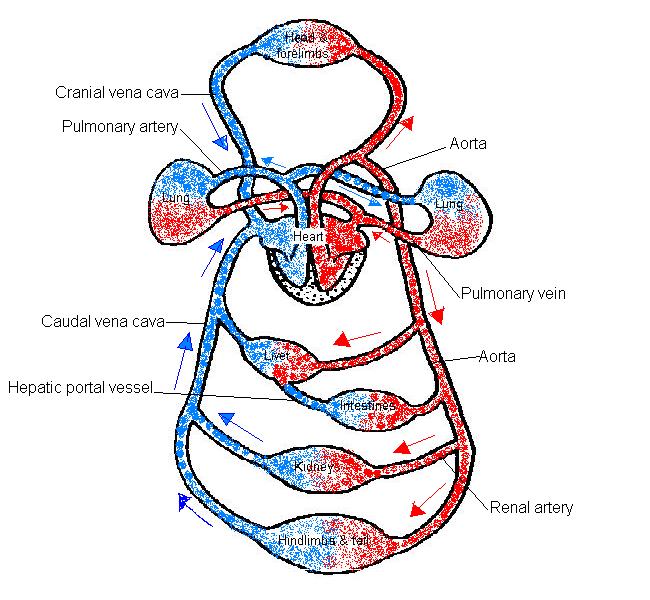
1.The diagram beneath shows the chief vessels of the blood circulation system of a mammal.
- a) Add the following labels to the diagram below:
- caudal vena cava; cranial vena cava; aorta; hepatic portal vessel
- pulmonary artery; pulmonary vein; renal artery
- b) Add arrows to show the direction in which the blood flows
- c) Colour the vessels that carry oxygen rich blood "blood-red" and oxygen poor blood "blue".
two. Arrange the following types of claret vessel in the correct order as blood would flow down them from the centre to the torso and back to the heart over again.
A. veins; B. venules; C. capillaries; D. arterioles; E. other arteries. F. vena cava; G. aorta
| Middle | Aorta | Other arteries | Arterioles | Capillaries | Venules | Other veins | Vena cava | Heart |
|---|
3. Make full in the blanks in the following table on arteries, veins and capillaries.
| Arteries | Capillaries | Veins | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure of wall | 3 layers | i cell thick | 3 layers |
| Thickness of wall | Thick | Very thin | Thin |
| Retain shape or collapse when no claret passes | Retain shape | Collapse | Collapse |
| Management of blood flow | Away from heart | From arterioles to venules | Towards eye |
| Speed of blood menses? | Fast | Becoming slower | Wearisome |
| Blood pressure level | High | Decreasing as flows forth capillary | Low |
| Valves present? | No | No | Yep |
| Pulse present? | Yep | No | No |
| Carry oxygenated/deoxygenated claret? | Oxygenated except pulmonary artery | Blood gives up oxygen as moves along | Deoxygenated except for pulmonary vein |
iv. The photograph below shows cantankerous sections through an artery and a vein.
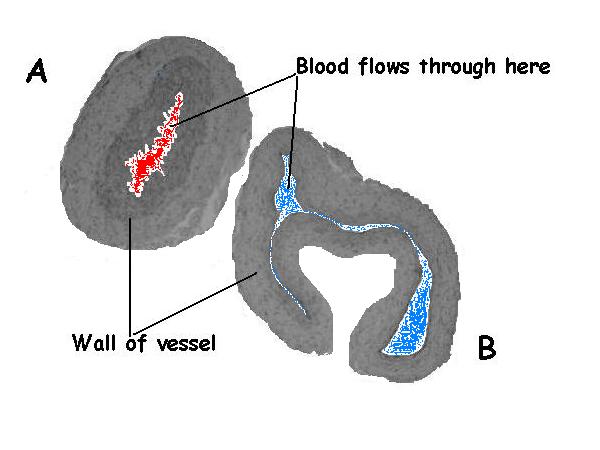
- a. Label which vessel is the artery and which the vein. A is the avenue and B is the vein.
- b. Requite two reasons for your answer.
-
- Reason 1. Assuming these are not the pulmonary artery and vein the vessel with carmine oxygenated blood is the avenue and that with bluish deoxygenated blood is the vein.
-
- Reason 2. The vessel with the thicker wall is the artery.
-
- Reason 3. The vessel that appears complanate is the vein as its walls are much thinner than those of the artery.
v. Truthful or false? If false give the right answer.
-
- Mammals have a double open blood organization. T
-
- Arteries but carry oxygenated blood. F The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood.
-
- Artery walls accept many more layers of tissue in them than the walls of veins. F Both arteries and veins have the same 3 layers of tissue in them. The difference is that the layers are much thicker in arteries as they demand to withstand the passage of high force per unit area claret.
-
- The pulse is only felt in arteries. T
-
- Arteries have valves in them to stop the blood flowing backwards. F Veins accept valves as there is no pulse and the blood is at low pressure then there is a tendency for the blood to pool or menstruation backwards.
-
- Blood leaks out of capillaries and then that the oxygen and glucose etc. tin reach the cells. F Many substances in the blood pass through the capillary wall to enter the tissue fluid that surrounds the cells. These substances motility across past various processes but the blood tin can not exist said to leak out of undamaged capillaries.
-
- Diastole is the stage betwixt pulses. T
-
- Blood flows along veins dorsum to the middle because of gravity. T Gravity may assist blood flow in veins located to a higher place the centre only generally virtually of the motion of claret in veins is brought most by contraction of the surrounding muscles.
vi. The diagram below shows the changes in the blood force per unit area during the passage of the pulse along an artery.
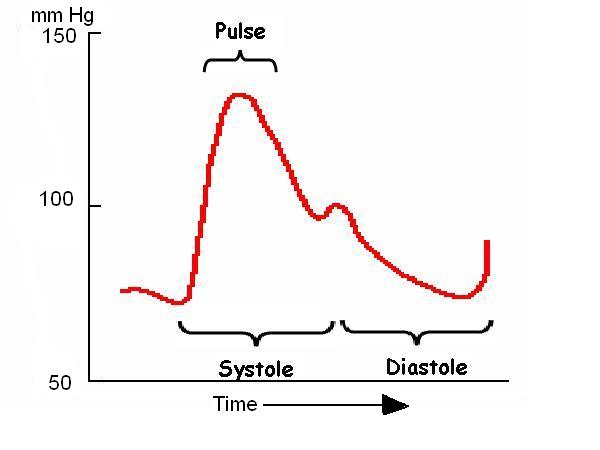
- Add labels to the diagram to show: the pulse; diastole; systole.
7. As at that place is no pulse in veins, what moves the blood along them? (Give at least 2 methods)
- 1. The contraction of the muscles surrounding the veins.
- 2. Gravity.
- 3. The contracting center pulls blood along the veins towards it.
8. Name the vessel that:
-
- Carries oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The coronary arteries.
-
- Supplies the encephalon with oxygenated blood.The carotid artery.
-
- Carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.The pulmonary artery.
-
- Carries blood from the intestines to the liver. The hepatic portal vessel.
-
- Carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys.The renal vein.
9. Await at the diagram below and then answer the following questions.
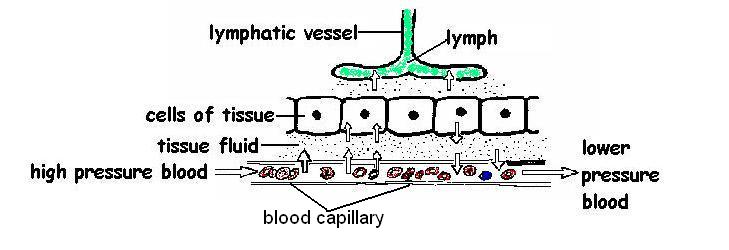
- a. Which is the blood capillary? Come across diagram.
- b. How thick is the wall of the capillary? Very sparse -i cell thick.
- c. What is happening to the claret pressure as the claret flows along the capillary? It decreases.
- d. What substances pass out of the capillary walls to surroundings the tissues? Water, oxygen, salts, amino acids, glucose, etc.
- eastward. What is tissue fluid? It is the clear fluid that surrounds the cells of the tissues It is formed from blood plasma.
- f. Which vessel is the lymphatic vessel? See labeled diagram.
- g. How do lymphatic vessels differ from capillaries? They are similar in construction having walls simply one prison cell thick. The chief difference is that capillaries deport blood whereas lymphatic vessels behave lymph.
- h. What passes into the lymphatic vessel? Tissue fluid passes into lymphatic vessels and (Hey Presto!) it becomes lymph
- i. How does lymph differ from tissue fluid? Both take a like constitution. The main difference is one of geography. Tissue fluid surrounds the tissues while lymph flows in lymphatic vessels.
- j. Why does the fluid leave the capillary at the beginning of the capillary bed and flow back in at the other stop? This is quite a complicated question probably above the level required simply here goes. The tissue fluid leaves the capillary at the arterial end because it is forced out by the high blood force per unit area. At the other end of the capillary the blood force per unit area is lower and because water has left the capillary at the arterial stop the blood in it is more concentrated. This means that the water outside the capillary is "pulled" into information technology by osmosis. Click here to find out more.
Return to Circulation Worksheet
Render to WikiEducator Anatomy and Physiology of Animals
scottbuthadou1985.blogspot.com
Source: https://wikieducator.org/Circulation_Worksheet_Answers
0 Response to "Hey Travel From the Heart to a Capillary Bed and Back to the Heart Again"
Post a Comment